Each day, approximately $5tn of forex trading is conducted in the currency markets. Trading one currency against is arguably the most popular forms of investing with participants ranging from super-sized hedge funds to small retail traders.
YOUR CAPITAL IS AT RISK

There are also a wide range of strategies used. Some use Fundamental Analysis to take a medium- to long-term view on the relative strength of economies (and their currencies). If the Australian economy, for example, is expected to outperform the US one, then the price of the Australian dollar in relation to the US one will increase. Others adopt a more speculative approach and use Technical Analysis to trade short-term anomalies in price caused by market ‘noise’.

There are lots of strategies to choose from and a wide range of markets on offer, which makes it easy to find one that fits in with your plans. The popularity of forex trading also means it’s possible to take advantage of freely available news, research and learning materials all designed to help you on your trading journey.
This review of how to trade forex in Singapore will look at specific market conditions and introduce some tips from experienced traders. It will outline how to find a trusted broker, what booking a trade really means and some safety checks to help you do it safely. First off, it’s worth asking the question, why is forex trading in Singapore so popular?
USDSGD – Daily Price Chart
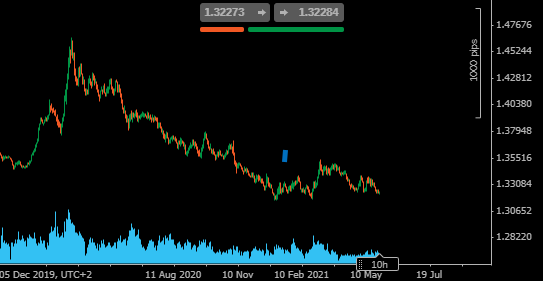
Source: Pepperstone
Table of contents
Why Trade Forex in Singapore?
Ease of Access
One of the main attractions of forex trading is how easy it is to set up an account and trade. The huge size of the market means that thousands of online brokers support trading in forex markets. As the market is unregulated, there is no central exchange or clearing house. Instead, trades are carried out over a network of interconnected parties. It’s trading in its purest form.
24/5 Trading – Trade Any Time You Want
Another neat feature of forex markets is that they can be traded around the clock. The absence of any centralised body overseeing trading means that there are no market hours. Instead, the buying and selling continues at times of day that suits those people who want trading to fit in with their lifestyle, not disrupt it.
USDSGD – 5-minute Price Chart – Trading 24/5
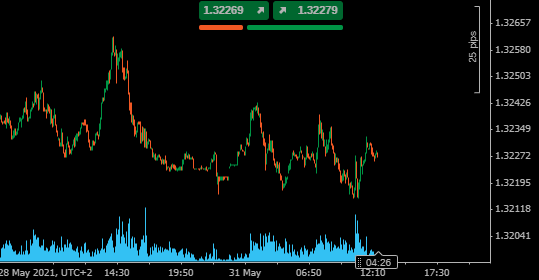
Source: Pepperstone
The fact that markets don’t close also means there is less ‘gapping’ risk. The time interval between equity markets closing and reopening, again, makes risk management harder to perform. Any stop-losses on your position are ineffective and invalid if the market opens dramatically down.
Liquidity & Pricing
Specialist forex broker FXCM estimates that approximately $33bn of trades are carried out in the Singapore dollar / US dollar, currency pair. This volume of trading in SGDUSD means that pricing is efficient. With so many participants, it’s impossible for any one party to try to manipulate the market, the wall of cash flowing through the market would just overwhelm them. The huge liquidity levels not only help keep traders honest, but it also results in competitive pricing.
The bigger the market, the easier it is for brokers to offer tight bid-offer spreads – the term used to describe the difference between the buying and selling price.
Forex markets are recognised as offering some of the most cost-effective trading. There’s no need to pay exchanges for the right to trade, there’s a lot of competition between brokers and the markets are massive. Stacked up, these cost benefits make forex trading a low-cost proposition, and that circles back round to mean traders keep more of any profits they make.
Market Transparency
If you’re looking to trade any of the major currency pairs, you’re entering a market where information is freely available. You might not make the right call, but it is unlikely that you’ll get caught by a sucker punch. Trading most stocks offers a similar degree of comfort, but prices in some small names can be distorted by information only known to insiders. If liquidity in those markets dries up, then not only do bid-offer spreads widen, but you might struggle to get out of a position altogether.
Low Barriers to Entry
It’s possible to start trading forex with only a few dollars and most brokers accept minimum deposits in the region of $100. Trading in small size is particularly useful for beginners and experienced traders trying out new strategies. If things go wrong, the financial impact can be minimised and by trading in small size and taking the emotion out of trading, you are improving your chances of success.
Quirks of Forex Trading
One of the quirks of forex trading is that prices can go down as well as up with equal ease. This can seem strange because all prices can swing both ways, but understanding the nature of equity markets helps explain how forex pricing works. Historical data points out that stock prices are associated with long-term upwards price moves and sudden price crashes. It’s just the way stocks have traditionally operated and is a function of equity prices being based on potential future earnings.
Forex markets can also record dramatic price moves, it’s just that there isn’t an underlying bias to move one way and not the other.
Well-established
The long-track record of forex trading has seen operators develop additional services which cater to particular tastes.
The first is in terms of automation. A lot of forex brokers allow clients to trade forex using algorithmic programs, which take some of the emotion out of trading and results in a more hands-off trading experience. It’s possible to design your own using programming wizards or use models provided by others in the trading community, some of which are offered free of charge.
Another way to get exposure to the forex markets. but limit the time you have to devote to carrying out your own research is Copy Trading. This involves hooking up your account to take signals from a third party. When they trade, so will you. The process is automated and relationships can be broken at the discretion of the follower. It doesn’t remove the risk that the lead trader might also make a wrong call, but it is an increasingly popular way for beginners to enter the market.
One important note is to ensure you don’t send funds to a scam operator. Regulated brokers such as eToro offer the service by operating a system where you remain in charge of your account and your cash but only take the signals.
What are Currency Pairs?
Any currency can be traded against another. The volume of trading is a result of historical and business relationships and those pairs which are most actively traded are termed ‘Majors’.
- The Australian dollar and US dollar: AUD/USD – ‘Aussie’
- The New Zealand dollar and US dollar: NZD/USD – ‘Kiwi’
- The US dollar and Japanese yen: USD/JPY – ‘Gopher’
- The euro and US dollar: EUR/USD – Euro-Dollar or ‘Fiber’
- The British pound and US dollar: GBP/USD – ‘Cable’
- The US dollar and Swiss franc: USD/CHF – ‘Swissie’
- The US dollar and Canadian dollar: USD/CAD – ‘Loonie’
The next category of pairs is the ‘Minors’ and include:
- EUR/JPY – Euro/Japanese yen
- CHF/JPY – Swiss franc/Japanese yen
- EUR/NZD – Euro/New Zealand dollar
- EUR/AUD – Euro/Australian dollar
- AUD/JPY – Australian dollar/Japanese yen
- NZD/JPY – New Zealand dollar/Japanese yen
- EUR/CHF – Euro/Swiss franc
- EUR/GBP – Euro/British pound
- CAD/JPY – Canadian dollar/Japanese yen
- GBP/AUD – British pound/Australian dollar
- GBP/JPY – British pound/Japanese yen
- GBP/CHF – British pound/Swiss franc
- GBP/CAD – British pound/Canadian dollar
- EUR/CAD – Euro/Canadian dollar
The final group is termed ‘Exotics’. SGDUSD is typically considered to be part of the group, but as the huge daily trading volumes prove, even ‘exotic’ markets can be liquid, easily traded and associated with low fees.
- USD/SGD – US dollar/Singapore dollar
- USD/HKD – US dollar/Hong Kong dollar
- EUR/TRY – Euro/Turkish lira
- USD/SEK – US dollar/Swedish krona
SGDAUD Daily Price Chart
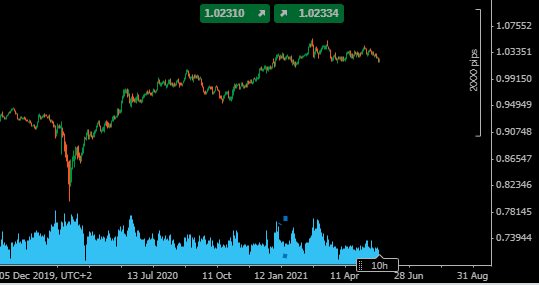
Source: Pepperstone
Each of the currency pairs have their own characteristics. USDJPY is traditionally a low volatility market. Seen by traders to reflect the potential for the US and Japan central banks to increase or decrease interest rates. It’s a slow-burner and even has its own name. the ‘carry trade’.
AUDUSD and NZDUSD are, in contrast, much more likely to experience dramatic price moves. Geopolitical tensions, for example between Australia and China, increase the risk of Australia losing access to a key export market. The suggestion that there could be a sudden drop in demand for Australian products then results in a drop in demand for AUD.
It’s worth establishing which type of market is a best fit for you. It will largely come down to your approach to risk and how active a trader you want to be. One way to work through that process is by setting up a demo account and practising trading. Demo accounts take seconds to set up and allow you to trade real prices, using virtual funds. It’s a great way to test-drive the functionality of trading platforms until you find the one you want to stick with. It also allows you to test trading strategies and get up to speed with the mechanics of trading.
How to Trade Forex in Singapore
The online trading platforms provided by brokers are a happy combination of easy-to-use functionality and powerful software tools. The number of forex markets on offer vary from broker to broker, as do the exact trading T&Cs, but the process of putting on a trade generally follows a similar format.
Before putting hard cash into any account, it is important to establish the trustworthiness of the brokers you are considering. If you don’t, you might lose all your money to a scam.
1. Choose a Broker
One way to assess a broker is by how long it had been operating. A broker that has been around for five or more years has very likely established how to run a viable business and had time to develop its platform to suit its clients. You can also consider online feedback from clients and trust ratings. The best method of checking if your broker is legit is to look for confirmation, they are regulated by one of the below Tier-1 financial authorities.
- The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
- The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA)
- The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC)
- The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
- Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC)
Even though the forex markets themselves are unregulated, using a regulated broker will be a sign that the firm you are using has met some stringent requirements. Financial authorities such as MAS only issue licenses to brokers that agree to comply with costly and time-consuming protocols. These include the need to submit business plans that demonstrate a business is viable. They are also subject to independent audits and have to ensure they have sufficient capital on account to limit the risk of them going bust.
As and when the regulator, such as MAS decides to adjust the rules and regulations, the brokers have to come into line. That means threats to the financial system are constantly being addressed.
2. Open and Fund an Account
Opening an account can be done completely online and even using a handheld device as well as a desktop.
The first step towards opening a live account is to supply personal details and ID verification. This will help you ensure you, and only you have access to the funds in the account you are setting up. The second stage involves answering a series of questions about your investment objectives and trading experience. These are so the broker can build up a profile for you and comply with their Know Your Client (KYC) protocols. Onboarding can be completed within a matter of minutes and you are then ready to transfer funds into your new account.
The exact details of the MAS policy on the subject of anti-money laundering (AML) can be found here. AML regulations provide an extra layer of security for broker clients. Rules designed to prevent international criminals moving money through accounts stipulate that any funds paid into a brokerage account can only be returned to the account from which they originally came. Clamping down on international crime is obviously a good thing in itself, but a neat side-effect is that a regulated broker just can’t forward your funds on to a scammer.
Transferring funds to your new brokerage account has the feel of any other online transaction. Most brokers offer in the region of eight different payment methods with credit / debit card and bank transfer being popular options. It’s worth checking the exact T&Cs to ensure you establish how long the payment might take to process and if there are any admin fees incurred. Shopping around in this area can save you time and money. Once the funds hit your account, you’re ready to trade.
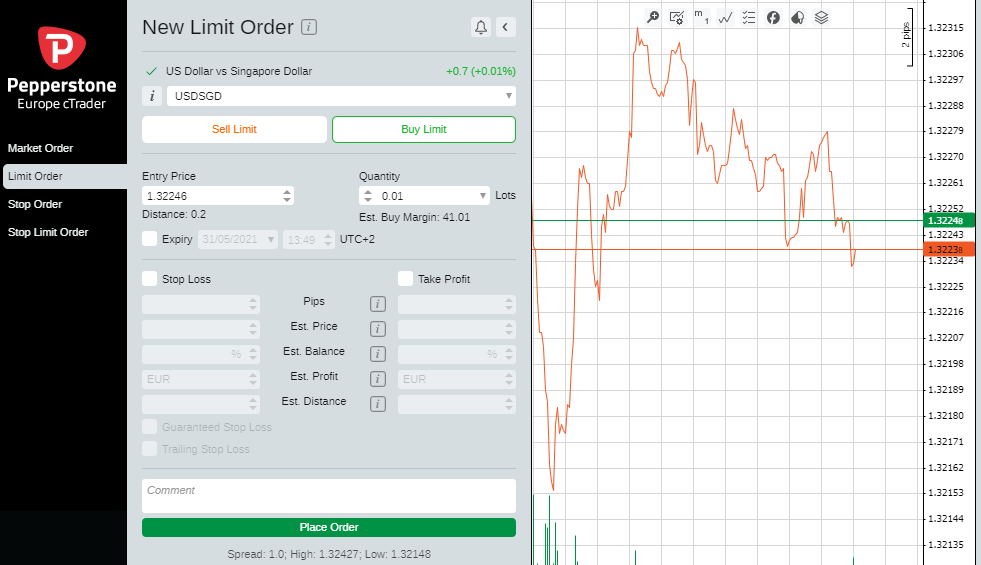
3. Open an Order Ticket and Set Your Position Size
After registering your account, the next step is to head to the forex market monitor.
Trade execution in the purest sense comes down to clicking on the market, inputting the amount you trade and clicking ‘buy’ or ‘sell’. It can be as straightforward as that, but there are some risk management tools to consider using prior to making the final click of the mouse or tap of the screen.
Source: Pepperstone
4. Set Your Stops & Limits
Stop Loss instructions and Take Profit orders are automated instructions you can build into the system to trade on your behalf if price reaches a certain level. You can set them up to trade you out of all or some of your position and they can be added at the time of trade, or any time afterwards.
Stop-losses are designed to close out loss-making positions. By cutting your losses, you live to fight another day and hope that winning trades repair the damage to your P&L (profit and loss).
Take Profit orders lock in gains by closing out positions that go your way. A hybrid approach is to use trailing stop losses. This involves setting a stop loss some way behind a winning trade. That way, hopefully, you won’t give back all of your gains, but leave the way clear for a profitable position to keep on running.
‘Stop-losses’ and ‘take profits’ are often recommended for beginners and popular among those trading short-term strategies. They can be an integral part of some strategies with stop-losses set just the other side of support or resistance price levels.
Another way to manage risk is by adjusting position size. If price in NZDUSD is whipsawing due to an imminent central bank announcement then instead of risking being stopped out by a price-flash move, trading in small size can allow you to remove stops from the system until the market stabilises.
Source: Pepperstone
There is one final order type to mention, ‘limit orders’. These allow you to state a price at which you want to buy a particular stock. They are binding contracts and might not be ‘filled’ if price doesn’t reach your target level. If USDSGD is, for example, trading at $1.3255 but you think it will clip the $1.3205 price level before heading upwards, you can build an instruction to trade at the lower level. There’s no guarantee you won’t miss out, but patience can sometimes be rewarded and allow you to enter a trade more elegantly.
5. Make Your Purchase
The final stage of the forex trading process is clicking the ‘buy’ or ‘sell’ button. At that point, some of the cash in your account will be exchanged for other currencies. In the case of a buy of SGDUSD, you would be long Singapore dollar and short US dollar. The broker manages this part of the process and if you’re trading using CFDs your position will simply report P&L according to the price moves in the market.
The ongoing performance of your position can be tracked using the ‘portfolio’ section of your site and this is also where you’ll be able to trade out of your position when the time is right. Checking the portfolio and your trade straight after trade execution is highly recommended. Even experienced traders make manual errors, and the golden rule is to spot and correct these as soon as possible.










