Trading currency markets using computer programs is increasingly popular, and for many, profitable. With trading platforms offering such a comprehensive service, it’s possible to set up your own algorithmic models or use the ‘robot’ signals provided by third parties. It’s an interesting approach and understanding the basics can make you a better trader even if you don’t ultimately use the method. This article will explore automated trading by looking at the following:
- Why is automated trading so popular?
- How does automated trading work?
- What does automated forex trading look like?
- What are good tips for starting out in automated trading?
- Getting started with automated forex trading
- The truth about automated trading
Why is automated trading so popular?
The attraction of trading using computer models is fundamentally down to two factors. The first is that it works — traders can make a profit trading systematically. The second reason is that it’s continuously being made easier to do.
The hedge-fund MAN Group estimates that 34% of the total hedge fund assets under management (‘AUM’) are currently managed by funds that run automated programs. In cash terms, this amounts to approximately $1,019bn in total AUM.
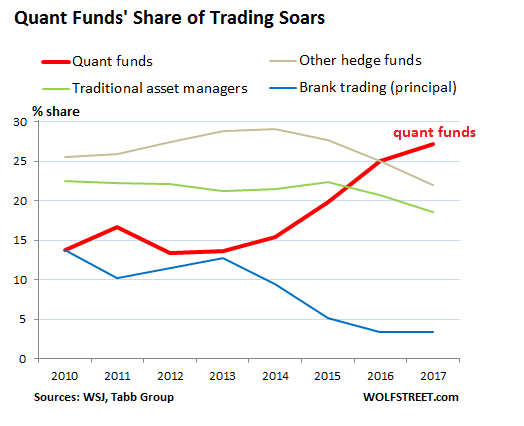
The world’s most popular trading platform for retail clients is MetaTrader’s MT4 system, which is the go-to platform for independent traders looking to automate their activity.
The history of automated trading
Automated trading made its way into the markets at the end of the last century. At first, it was via a semi-automated approach. Any computer that takes in data from live markets can ‘listen’ to the market, crunch numbers faster than a human, and generate a buy or sell signal.
In the early days, these signals required human intervention, but nowadays the entire process is automated with each stage, including trade execution.
Benefits of automated trading
Many of the perceived benefits and disadvantages of automated trading are two sides of the same coin. The fact that it is ‘unemotional’ and involves no human interaction can be a positive or negative depending on your point of view. The supporters of robo-trading will gladly explain that it involves:
- Trading discipline— It removes the potential for emotion-driven human intervention
- Data driven— Human brains are hard-wired to make trading errors. Beginners often run loss-making trades in the hope they come back into profit. Systematic trading is entirely model driven
- Less trading errors— Manual trading is open to operational risk such as ‘fat finger’ errors when booking a trade
- Less intensive– Once your model is up and running, you will likely find you are able to take a more hands-off approach to trade management
Disadvantages of automated trading
Developing a trading psychology involves adopting a critical approach to any ‘sure thing’. Automated trading is no different and it’s important to know some of the challenges faced:
- System meltdown— Technological advances make this less likely, but there is still the question of what happens if your trading signals go ‘haywire’
- Crowded trades— If everyone is using the same data and the signals are so well known, what happens if millions of other traders follow them?
- Space race — Some systematic trading strategies require high-level tech knowledge and substantial investment in hardware
- Other costs — All strategies need a clear cost analysis, and if you’re taking on extra charges from third parties and data providers these can stack up
- Slippage — This term explains trades not being executed at the price the model predicts. Markets are a dynamic environment and the order to trade might not be filled at the intended level
- The ‘fundamental’ problem — Can technical analysis alone generate returns? How do data points like moving averages cope with sudden changes to ‘fundamentals’in the form of geopolitical events and natural disasters?
- Paradigm shift— This is the big one. Trading solely off the back of historical data does not guarantee future returns. Things change and you might not know that until you’ve blown up your account
How does automated trading work?
Automated trading involves using computers to analyse market data such as prices and then turn that information into trading ideas. It involves using a program that executes trades according to pre-set rules for entering and exiting trades.
The processes could be completed by hand, but system-based analysis is much quicker. This means more variables can be considered because by the time all of the information is collated, price may still be at a level that confirms a trade is still a good idea.
Calculating multiple variables manually and coming up with the conclusion that a buy trade is appropriate is little use if price has moved to a higher level in the mean-time.
Statistical data often used in developing automated models includes:
- Moving Averages
- Fibonacci retracement levels
- Bollinger bands
- Trade volume — The higher the volume, the greater the weighting given to a signal
- Support and Resistance levels — For example, the days intra-day lowest and highest price
- MACD
- Oscillators
The above list is just a sample, and some models incorporate data on a massive scale. Much of the above works on the basis that price can over-shoot and therefore be liable to fall back at some point.
Other models pick up on momentum signals and try to catch a ride on a price move.
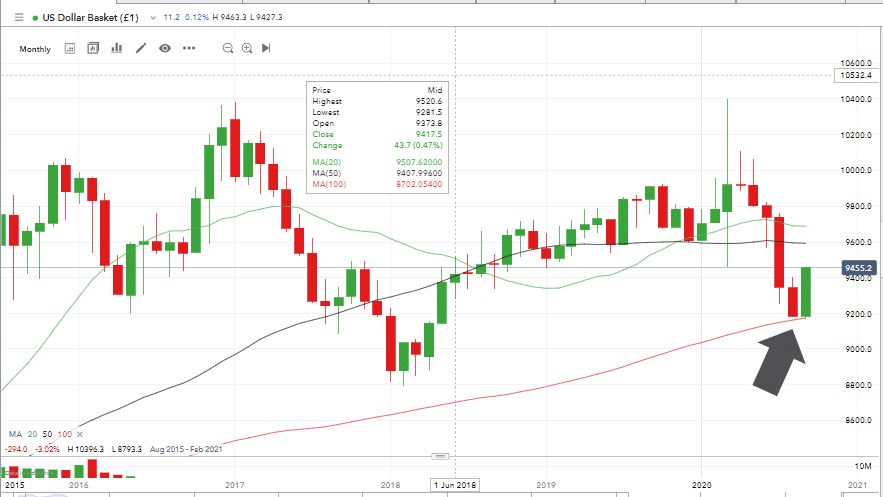
Source: IG
The above chart shows the price of the US Dollar Basket (USD vs a group of other currencies) touching the monthly 100 SMA (Simple Moving Average). The SMA acts as a support for price, which then rebounds. Automated trading models continuously consider these and other multiple variables.
What does automated trading look like?
If you’ve been on an online broker and tested a demo account manually, you’ll have an understanding of the life of a trade.
With automated trading, the process is done for you and realistically, the majority of any time you spend monitoring your trading will be reviewing your portfolio, and tracking profit and loss on positions.
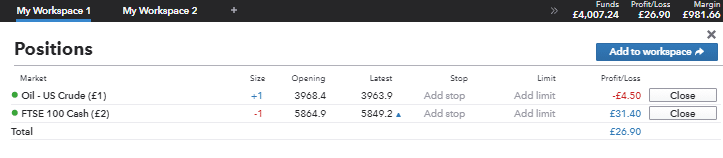
Source: IG
It’s important to remember that you still need to keep a check on your trading. With automated trading, the likelihood of a malfunction is low, but the consequences associated with one are high impact.
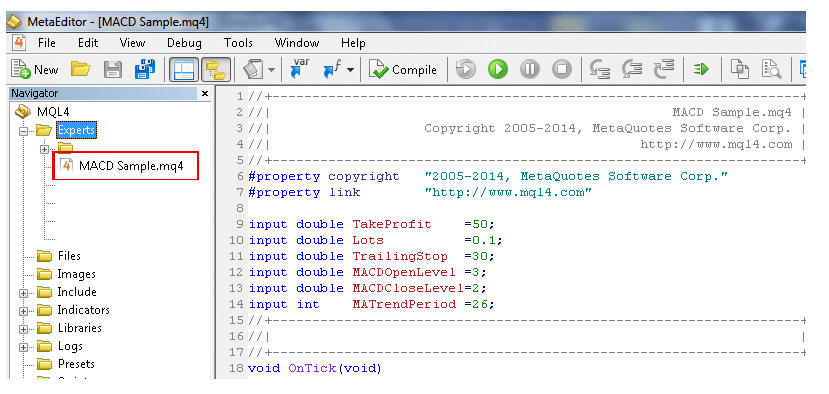
Source: MQL4
The process of developing your models and hooking them up to a trading platform is worthy of its own research note. Take comfort from the fact that brokers provide ‘wizards’ and other such tools to help you get your models up and running.
You can deep-dive into granular levels of code if you want to, but it’s certainly not necessary.
What are good tips for starting out in automated trading?
Take a tip from the professionals. The established stages of trade modelling are:
- Idea generation
- Research
- Backtesting
- Demo trading
- Optimisation
- Demo trading
- Implementation
- Optimisation
- Live trading
Optimisation is a stage that is repeated. It involves going back a number of stages and re-configuring the trading model based on its performance. It’s worth noting that ‘over-optimisation’ is a common pitfall for traders. A ‘perfect’ model can be an ideal way to trade historical data, but not much use when trading future market conditions.
A model will not be approved for the next stage purely on the basis that it is profitable. A program that makes money, but not for the right reasons, could be very dangerous to apply.
Implementation is the process of applying the model in a real-time, and more importantly, real-money environment.
There are lots of small differences between demo and live trading systems, which can mean a model that works in demo mode doesn’t work in the real market. During the Implementation stage, trade size will be small and only scaled up after each level of optimisation is completed.
Getting started with automated forex trading
There is an extensive number of third-party and in-house service providers in the market looking to hook you up with automated trading systems.
A few good places you might want to start are:
- MetaTrader — MT4and MT5 — A long-time market leader in services relating to automated forex trading
- Expert Advisors– Part of the MetaTrader suite of services, whereby the user doesn’t develop and apply their own models but takes automated trade instructions from third parties
- Copy trading — Apply trading signals from other traders automatically to your account. Available at brokers such as eToro
Source: MT5
Final thoughts
There is a tricky balance between trusting the models and manual intervention. A lot of the skill involved in successful robo-trading involves getting that right.
Staff of big systematic hedge funds will sell you the idea that the model can be trusted. A track-record shows that market-beating returns is likely to attract investors.
At face value, it appears that the smart guys are having fun making money. But it’s hard to know what happens behind closed doors. Don’t be fooled into thinking that, from time to time, the plug doesn’t get pulled.
This doesn’t mean automated trading doesn’t work, just that you need to know how it can work for you.
Being too greedy can lead to ‘over-optimisation’ of your own models or lead you into the hands of unscrupulous third-parties offering something that is ‘too good to be true’.
Developing and testing models in a demo account is, in its own way, a very valuable process. With such a large proportion of the market using automated trading techniques, gaining an understanding of what’s going on in the other room is going to benefit you, even if you adopt a manual ‘discretionary’ approach.













