A Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) policy is a written and public commitment made by a company, such as Google owner Alphabet, that outlines how it intends to manage the social, environmental, and economic effects of its operations. Firms often make specific targets and update investors on their progress towards achieving them.
YOUR CAPITAL IS AT RISK

A poor or even apathetic approach to the subject can be bad for a firm’s share price. CSR is an important part of the investor decision-making process, with retail and institutional investors all increasingly aware that it’s a trend that is building momentum. This article will explore the Google CSR policy.
What is Corporate Social Responsibility?
The most frequently used benchmark in terms of CSR policies is the one outlined by the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO). The document known as ISO 26000 draws on the thoughts of that independent organisation and offers guidance on what good practice would be. ISO 26000 is not a set of hard and fast rules, which means firms can’t achieve ‘certified’ status. Instead, they have to interpret the guidance and address the issues in a way that satisfies investor demands and public opinion.
From an investment perspective, it’s important to establish if a firm’s targets are ambitious enough and if it is meeting them. Reports on both of these variables tend to be released annually and can change over time, but the key take away is that any slip-ups can be bad for the share price.
Businesses that get caught on the wrong side of the line can find their reputations battered and even face consumer boycotts. Those who get it right can see their share price rise thanks to buying pressure from the ever-growing number of investors who are monitoring green credentials.
What is Google’s CSR Policy?
The first point to make about Google’s CSR policy is that it is backed up by hard cash. Like other firms, it also has long-term aims relating to such things as carbon emissions, but the here-and-now of the situation is that the firm has already provided more than $100m in grants and investments.
Big spending is part of the solution, but the firm’s CSR policy also addresses specific parts of its business model, which, in places, are energy-intensive. Cutting back on its footprint is a clear objective, but the policy also references the benefits of its core business in terms of helping the global economy become more efficient. Information is power, and the services that Google provides allow individuals all across the world to fact-find and make more socially conscious decisions as a result.
Sustainability across the Google network of companies and supply chains is headed up by Kate Brandt. She joined the firm after holding a similar position for the US Federal Government. Her mandate includes data centres, real estate, supply chains and product teams.
Environmental Policies
The ecological impact of Google’s operations is the biggest issue for the firm to contend with. Alphabet (Google) emitted approximately 10 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalents in 2020, according to Statista, which puts it in line with other tech giants such as Microsoft, which produced 10.9 million tons in 2020.
In response, the firm is the world’s largest buyer of renewable energy and has also launched initiatives such as its ‘high-quality carbon offsets’ program, which it claims has wiped out its entire carbon footprint. Google claims its policies have negated all the carbon the firm has been responsible for since its inception. Looking to the future, the firm also states that its day-to-day operations have been carbon-neutral since 2007.
Google isn’t just buying its way out of trouble by arranging for trees to be planted. In fact, the firm’s extensive self-analysis has led to it pretty much achieving its aim of building the world’s most energy-efficient computing network. On average, Google data centres are twice as efficient as a typical enterprise data centre. This kind of innovative, forward-thinking, backed up by a willingness to invest in long-term energy-saving plans, makes the firm stand out from its peer group.
Social Policies
Google’s operations are relatively self-contained. It does have some degree of exposure to the risk of sourcing materials from war zones or factories using child labour but on nothing like the scale of rivals such as Apple.
It’s also seen as a good employer. Many of the brightest graduates would like to add the company to their CV. This strong bargaining position in terms of hiring staff has enabled Google to ensure that its workforce is moving towards its diversity targets. By 2025, it aims to have at least 30% of its leaders drawn from underrepresented groups with a focus on black, Latinx and Native American and is introducing racial consciousness programs for all employees.
Corporate Policies
Google has designed and implemented a plan to make its workplaces some of the best around. Its ‘Living Buildings’ project involves creating an ideal environment for staff. Work canteens focus on cutting down on waste, the buildings harvest water, and the ‘Healthy Materials Program’ considers what the Google offices are actually made of in an effort to cut down on staff coming into contact with potentially damaging materials during their working day. The London HQ is the first International Living Future Institute (ILFI) Zero Carbon-certified project in the world.
The firm promotion of ‘healthy and open discussion’ might or might not be a reality. It’s hard to know for sure, but statistics suggest that employees are well compensated, which will lessen the blow even if this isn’t the case. The average salary of Google staff is a market-beating $119,000, and the average annual bonus is $19,000.
Staff turnover is close to the industry average at 3.2 years. Considering Google staff are considered to be some of the brightest and most dynamic in the industry and much coveted by competitors, holding onto staff for an average amount of time is a sign that there isn’t any great discontent.
While Google doesn’t have as extensive supply chains as manufacturers of retail products, it still dedicates sections of its CSR to the subject. “We expect the highest ethical standards throughout our supply chain and promote meaningful social change at supplier sites and nearby communities” (Source: Google).
How Does Google Compare to Other Companies?
In terms of CSR policies, tech giants as a whole compare well when compared to traditional industries. The virtual nature of tech-stock products means they tend to have easily identifiable footprints, namely energy usage and the budgets to deal with them. Google doesn’t have many added complications of suppliers and sub-suppliers and the reputational risk that comes from finding, somewhere down the line, that its products are being made by forced labour.
Google, therefore, starts from a strong position but also goes one step further and ranks highly among the tech-stock peer group. The measures it has taken to remove its carbon footprint and approach to work environments are best in class. The only risk to its reputation relates to its dominant stronghold on the internet search market. In major markets such as the US and Europe, it accounts for approximately 90% of search traffic. The firm appears ready to address that issue and the CSR policy itself is part of its approach to managing any bad PR risks it faces and could lead to it becoming a victim of its own success.
How to Invest in Ethical Companies
Choose a Broker
Once you’ve made the decision to buy Google shares, the next step is finding the right broker for you. There are a lot of good brokers operating in the market, and the priority is to ensure your funds are safe. Google’s market capitalisation is of such a size that most brokers offer a market in the shares. So, fine-tuning your selection while prioritising reliability and trustworthiness will still leave you with an extensive shortlist.
AskTraders recommends choosing a broker that is regulated by one of the below Tier-1 financial authorities:
- The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA)
- The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC)
- The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
- Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC)
You don’t have to choose a US-based broker because of the global nature of trading. If you’re looking to buy Google shares from the UK or UAE, it’s easy to do and the process is very similar, whichever broker you choose.
Open & Fund an Account
The process of setting up an account and trading Google stock can be done completely online using a handheld or desktop device. It takes as little as 15 seconds to set up a demo account, with which you can practise trading virtual funds. To set up a live account and trade real money takes slightly longer as it involves working through a series of questions so the broker can build a profile for you. The good news is that once set up, you and you alone will have access to your account.
Some brokers offer up to 15 different ways to send funds to your new brokerage account. Debit and credit cards and bank transfer are among the most popular methods, and the former will usually be associated with near-instant processing speeds. The portals for making payments have user-friendly functionality and the process is similar to any other online purchase or banking transaction.
Another neat safety measure associated with regulated brokers is that to comply with anti-money laundering (AML) legislation, regulated brokers can only return funds back to the account from which they came.
Best Brokers to buy Google Stocks:
eToro: 68% of retail CFD accounts lose money
Take a lookTickmill: FCA Regulated
Take a lookIG: Over 16k stocks to trade
Take a lookIf you are ready to add some Google stocks to your portfolio you’ll need a broker that is regulated, has low fees and a user-friendly platform. Finding one can be a daunting task, which is why we’ve selected some of our favourites that tick all of these boxes to help you get started.
Research Companies Using Technical & Fundamental Analysis
Once you’ve established that Google’s CSR policy is strong enough to justify making an investment, it’s a case of optimising your trade entry point. The Google share price is a bit of a rollercoaster ride and applying a degree of patience can help you buy Google stock during one of its price dips. The use of technical analysis can help with that. It analyses historical price data and converts that information into metrics that monitor market momentum and identify trade entry points.
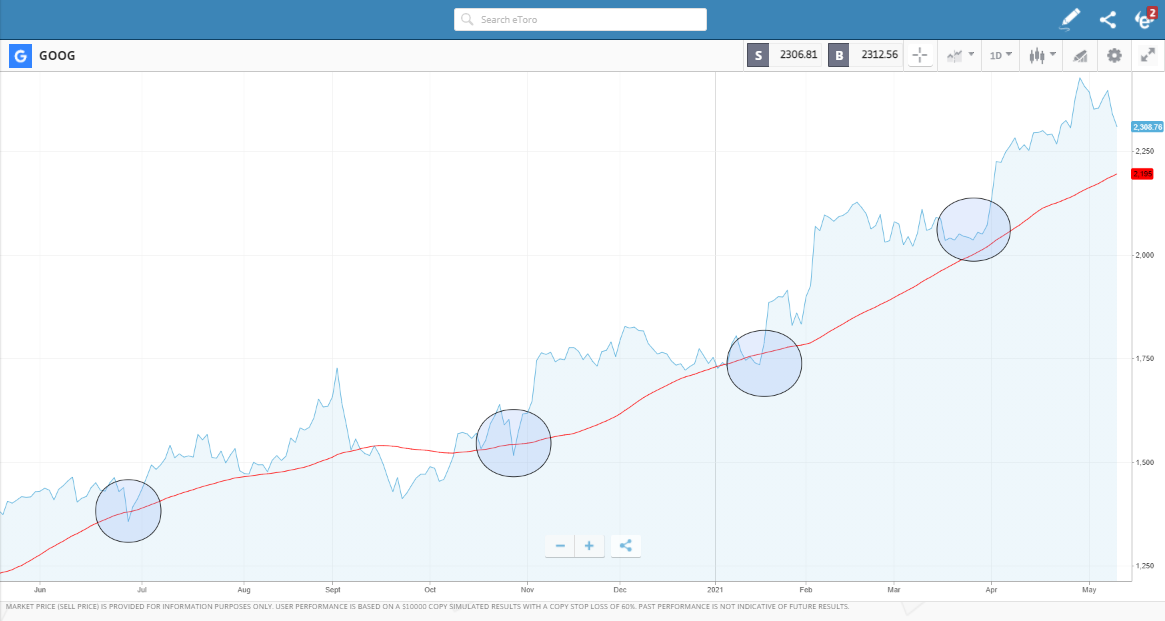
Fundamental analysis considers medium and long-term factors which could influence the Google share price. This could be announcements on market share, revenue growth or new product launches. A common approach is to use fundamental analysis to decide if you should buy a stock and technical analysis to decide exactly when.
The ‘Feed’ area of the eToro site is an example of Social Trading where clients of that broker can share their thoughts and ideas on Google’s prospects. The contributors to that area of the platform often post ideas, which incorporate both technical and fundamental analysis.
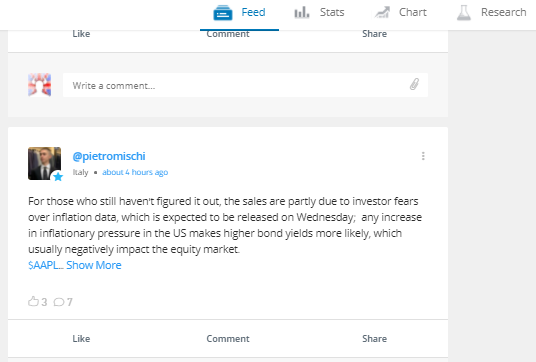
Source: eToro
Open an Order Ticket and Set Your Position Size
Good online broker platforms are a user-friendly combination of powerful software tools and intuitive functionality. There are slight differences between the different setups and trying some out using demo accounts is a good way to get hands-on experience.
The actual order tickets have data fields where you enter the quantity of Google stock you want to trade. In its simplest form, buying Google shares involves just clicking or tapping the ‘Buy’ button to execute your trade.
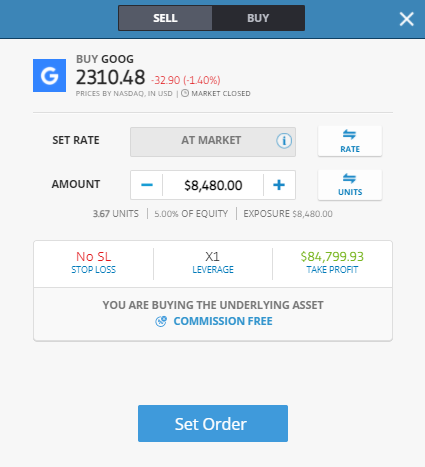
Set your Stops and Limits
Using Stop Loss and Take Profit instructions is an additional option. These are automated instructions to close out part or all of your position if the price reaches a certain level. The system will do the work for you and either cut a losing position to manage downside risk or close out a position at a gain to lock in some profits. If you’re a buy-and-hold investor looking to buy Google stock for the long run, you may want to manage risk by trading in small size and not using stop-losses. That way, you won’t get stopped out by temporary or short-term price dips.
Select and Buy Google Shares
The process of clicking ‘Buy’ will convert some of your cash balance into a holding of Google shares. At this point, that position will fluctuate in value according to live market prices. A top tip from experienced traders is to check your trade as soon as it’s executed. Even the pros make errors and these need to be identified and corrected as soon as possible.
Is Google an Ethical Investment?
Google has put hard cash into play to achieve the status of being an ethical investment. The headline figures, such as having negated the firm’s carbon footprint over the entire course of its history, are very impressive. Its highly profitable business model means investors can take comfort from the fact that there is a big budget available to manage any potential environmental or workplace CSR risks.
That same ‘highly profitable business model’ does have the potential to damage the brand due to the firm’s near-monopoly status in the internet browsing market. But it has to date proved adept at swerving any major issues. In the recent spat between internet giants and Australian publishing houses, Google took conciliatory steps long before Facebook did and left Mark Zuckerberg’s firm on the hook and in the middle of a bad PR storm. The last box to tick relates to day-to-day business operations and here Google again does well. The firm has shown a commitment to digging down to a granular level to, for example, make its servers some of the most efficient in the industry.
If you’re thinking of investing in Google and are weighing up the firm’s CSR credentials, then it’s also worth remembering that internet searches do also lead to global improvements in efficiency. The core business model can be considered to be making the world a greener place. Or as Google puts it, “the path to a cleaner, healthier future begins with the small decisions we make each day” (Source: Google).











