
What is the Put-Call Ratio?
The Put-Call Ratio is metrics used by traders as a way of assessing sentiment in the market, i.e. the overall attitude of traders towards an asset.
Essentially, it shows us whether traders are in a buying mood or a selling one. Put-Call Ratios show the relationships that exist between total put volume and total call volume on a given trading day.
What is a Put?
Put options offer traders the right to sell assets at a predetermined price and time (bearish trade)
What is a Call?
Call options offer traders the right to buy assets at a predetermined price and time (bullish trade).
How Is the Put-Call Ratio Calculated?
The Put-Call Ratio is calculated by dividing total put volume by total call volume over a specific period.

In most cases, traders will buy Put options when a decline in market valuation is expected.
In contrast, traders will buy Call options when a decline in market valuation is anticipated.
When a Put-Call Ratio is higher than 1, it shows that traders have purchased more call options than put options, and the indicator produces bullish trading signals.
When a Put-Call Ratio is lower than 1, it shows that traders have purchased more put options than call options, and the indicator produces bearish trading signals.
How Do You Use The Put-Call Ratio in Trading?
In the chart example shown below, we can see that traders are able to use the Put-Call Ratio to identify instances where trading volumes project bullish and bearish movements in market price activity.
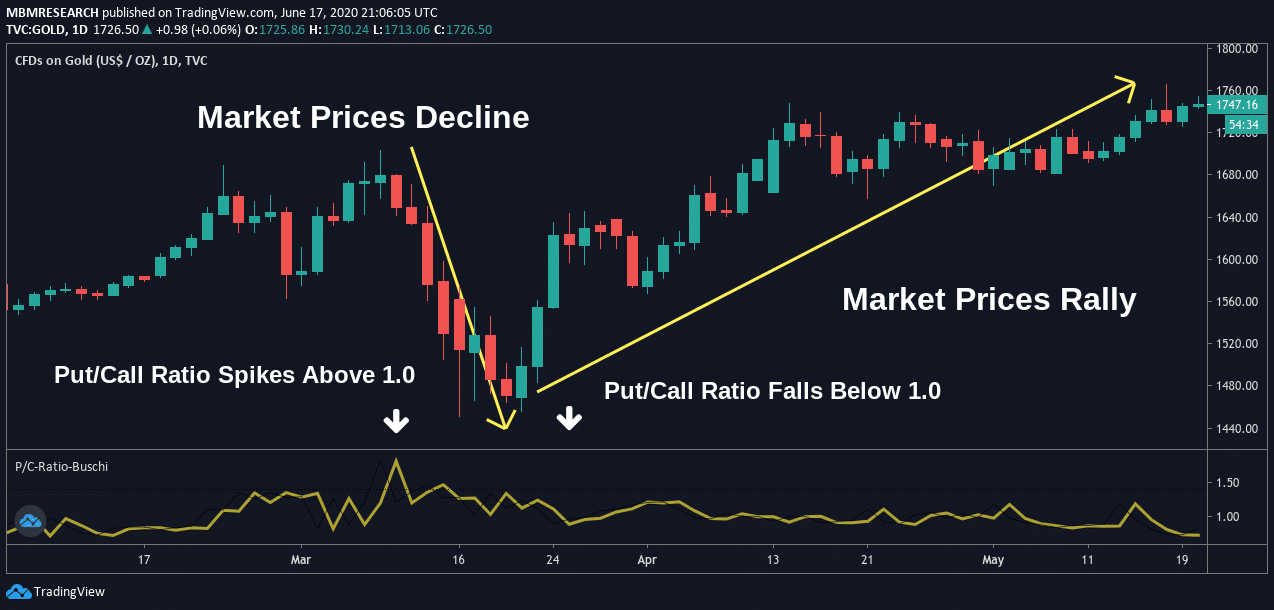
An initial spike in the Put/Call Ratio leads to a dramatic decline in price activity as the majority of the market positions for bearish trend movements.
Once these price moves unfold, the majority of the traders in the market develop a bullish interest in the asset.
This interest should not be surprising because valuations are cheaper, and this makes it easier for investors to generate gains through call options.
Near the middle of the chart, the bullish transactional volume begins to increase. Falling indicator readings in the Put/Call Ratio should act as a positive trading signal that can establish long positions.
Market prices begin to rally as the indicator plunges below the 1.0 level, and traders holding long positions can capture significant gains in the process.
Advantages
For technical analysis traders, the Put-Call Ratio helps to identify potential trend reversal points before they become visible in market prices.
The Put/Call Ratio, therefore, works as a hybrid tool that can be used in both technical and fundamental analysis strategies.
Trading signals are often most evident after corporate earnings reports or major macroeconomic events that have the potential to influence sentiment in unexpected directions.
For example, a disappointing corporate earnings report might lead to a new wave of put options associated with a stock. This can raise the Put/Call Ratio in ways that send bearish trading signals to the market.
Disadvantages
The Put-Call Ratio has limitations for traders with a specific focus on technical analysis strategies.
While the indicator offers an objective viewpoint of the dominant trading volumes that are seen in options markets, its trading signals are often short-term in nature.
As a result, they can sometimes miss specific price patterns that might be apparent using other forms of investment analysis.
For these reasons, it is often a good idea to include an additional momentum indicator as part of your analysis to achieve a broader assessment of the market’s price action.

Conclusion
The Put-Call Ratio is a unique investment tool that uses options trading volumes as a critical indicator of market sentiment.
Trading volume in call options is likely to increase before markets experience price rallies. At the same time, trading volume in put options is likely to increase before markets experience price declines.
In many cases, Put-Call Ratio trading signals will contradict prevailing market trends. This gives contrarian investors (those who deliberately go against the grain) an opportunity to establish positions that may not be apparent to the rest of the market.
Since the Put-Call Ratio is primarily based on fundamental trading data, technical analysis traders should also consider pairing it up with a momentum indicator.
An additional confirmation tool, such as a momentum indicator, creates a more comprehensive approach that is less likely to encounter losses over time.
PEOPLE WHO READ THIS ALSO VIEWED:




